Fractal Logic 📖
This section's goal is to introduce key technical concepts, enabling you to gain a deeper understanding of how Rsfrac works.
We will not delve into the details, as the goal is to provide a basic understanding. The explanations will be simplified and not entirely precise but sufficient for comprehension.
This section will cover the following topics:
- Complex Numbers
- Fractal Sequences
- Divergent and Convergent Points
- The Divergence Value
- The Bailout Distance
Complex Numbers
Complex numbers are numbers that consist of two parts: a real part and an imaginary part. They are written in the form a+bi, where a is the real part, b is the coefficient of the imaginary part, and i is the imaginary unit, defined as √(−1) . Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to a two-dimensional complex plane, where the horizontal axis represents the real part and the vertical axis represents the imaginary part.
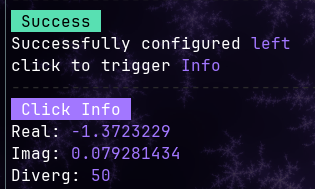
In the Rsfrac canvas, you can click on any point while the click mode is set to info to get the complex number associated with a pixel.
You can set the left click mode to info with this command:
click_mode left info.
Fractal Sequences
A sequence is an ordered list of numbers, known as terms, that follow a specific pattern. A sequence can be defined by its first term and the relationship between consecutive terms.
For example, the first terms of the v sequence, which is defined by v₀ = 1 and vₙ₊₁ = vₙ×2, are:
v₀ = 1v₁ = v₀×2 = 1×2 = 2v₂ = v₁×2 = 2×2 = 4v₃ = v₂×2 = 4×2 = 8
The position of a term in a sequence is referred to as its rank.
In the Mandelbrot Set, each point is associated with the sequence: Uₙ₊₁ = Uₙ²+P, where the first term u₀ is the complex number associated with the pixel.
Divergent and Convergent Points
When exploring fractals, we deal with iterative sequences derived from complex numbers. Each term in the sequence depends on the previous term, and as the sequence progresses, one of two things typically happens:
- Divergent points: These are points where the sequence grows indefinitely. As the iteration progresses, the magnitude of the complex number (its distance from the origin in the complex plane) becomes arbitrarily large.
- Convergent points: These are points where the sequence stabilizes, approaching a specific value, or staying within a certain bounded region of the complex plane. These points are colored black by default in Rsfrac.
The Divergence Value
If a term in a sequence exceeds a certain threshold (commonly called the escape radius), we consider the sequence, and therefore the associated pixel on the canvas, to have diverged. The rank of this term is called the divergence value, and it is used to decide how the point will be colored.
You can also click on any point while the click mode is set to
infoto get the divergence value associated with a pixel.
The Bailout Distance
The bailout distance is the predetermined threshold mentioned above. It defines when a sequence is considered to have diverged.